Tech Focus: Can Depression Be "Technology Malleable?"
Many things come to mind when mention is made of technology. Our discussion begins with assessing social media use and any potential correlation to depression. Multiple studies have been conducted regarding the increased use of social media and rates of depression among adolescents. When young people tend to immerse themselves in social media, studies suggest that elevated levels of depression are reported vs. groups of people who spend less time on social media.
Social media platforms like TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, and the like have been cited as provocateurs for elevated levels of depression. However, in 2017, a significant study (500,000+/- students between 8th and 12th grade) was undertaken. Among that population group, studies recorded elevated symptoms of depression between 2010 – 2015.
During the same timeframe, girls in that group experienced a 65% uptick in suicide rates. On a parallel track, a sharp rise in smartphone usage took place. Smartphones were introduced to students around 2007, and 92% of students had smartphones by 2015. Increased use of technology was strongly correlated with higher levels of depression in that population. The studies were undertaken by a team of psychologists headed by Jean Twenge, Ph.D. from San Diego State University.
Today's Young People Prefer Tech Over Face-to-Face Communication
It is noteworthy that today's generation of young adults spends significantly less time interacting with their peers in person than Generation X. This lack of face-to-face interaction profoundly affects psychological balance. When human connections are primarily conducted electronically, digitally, and at a distance, less emotional satisfaction is gained. This can lead to feelings of isolation, despair, and ultimately depression. As social beings, we crave the human touch. However, electronic communications can only satisfy our sense of belonging to a certain degree. The bonds that bind humans and build relationships cannot be fulfilled through a keyboard and a screen.
There are risks attendant with the increased use of technology. This is especially noticeable in the area of mental health and wellness. There are clear correlations between high use of technology and decreased social skills. Internet addiction is a significant concern for youngsters. There are strong links between this disorder and decreased physical activity, low self-esteem, mental health disorders, and societal functionality. Numerous studies suggest that the most impressionable sectors of society are most affected by excessive technology use, with attendant high rates of depression. This demographic is typically the 13 – 18-year-old age group.
This developmental phase in a young person's life is critical to shaping that person's future. Therefore, parents, caregivers, teachers, and role models are encouraged to help youngsters balance Internet use, technological reliance, physical exercise, education, nutrition, and adequate social interaction. Tell-tale signs of adverse effects of technology include mood swings, withdrawal, depression, inability to concentrate, risk-seeking behavior, poor dietary habits, sedentary behavior, and substance abuse et al.
Technology that Treats Depression
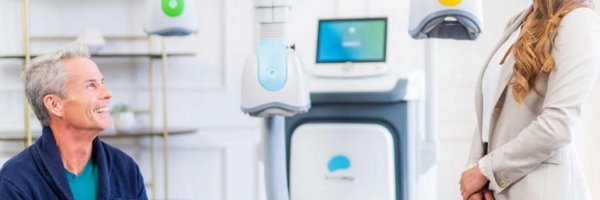
Doctors can also use technology to enhance the quality of life, remediate mental health disorders, and simplify complex life challenges. One such application is Deep TMS™ by BrainsWay. This cutting-edge technology utilizes a patented H-Coil helmet for treating depression. An estimated 40% of depressed individuals have what is known as treatment-resistant depression. When medications like SSRIs don't have the desired effect or have bad side effects, magnetic therapy for depression provides a workable solution.
Deep TMS is a breakthrough technological treatment that is FDA-cleared and used for treating MDD (major depressive disorder), anxious depression, OCD, and smoking addiction. The helmet-style device houses sophisticated technology comprised of coils that generate a magnetic field. These magnetic waves accurately target problematic areas of the brain to regulate neural activity. Deep TMS is a more sophisticated treatment than traditional TMS (which uses a Figure-8 coil) and more efficacious in terms of outcomes. This non-surgical, non-invasive treatment has limited side effects (restricted to minor headaches or tingling during treatment sessions only), with no need for anesthesia.
Individual treatment sessions are short (10 to 20 minutes), for five days a week, and last for 4 to 6 weeks at approved treatment centers across the country.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
Vagus Nerve Stimulation, or VNS, is a surgical alternative to treating depression. For people who are experiencing treatment-resistant depression, or chronic depression, the FDA has approved VNS. Of course, any surgical procedure carries inherent risks. The antidepressant properties of Vagus nerve stimulation take place over a prolonged period of time. A battery-powered device is implanted subcutaneously on the left side of the chest. Mild electrical stimulation is delivered to the Vagus Nerve by the battery-powered device. This technologically sophisticated treatment for depression is recommended for bipolar disorder and unipolar depression.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
ECT is another breakthrough technology that was discovered in the 1930s. The researchers found that electrical current stimulation in the brain resulted in mild seizures. These altered the brain's chemistry. Harsh at inception decades ago, ECT has become milder over the years so that patients can tolerate it better. During the treatment regimen, a machine transmits tiny electrical currents to the brain. This is conducted 2X weekly or 3X weekly over several weeks. The seizures last an estimated 30 seconds. ECT is effective for treatment-resistant depression, but it has many attendant risks. Anesthesia must be administered in a hospital setting. Memory loss and confusion can result.
|
|


